Augmented reality (AR) has rapidly evolved over the years, with two primary types emerging: namely marker-based and markerless AR.
Table of Contents
ToggleNow it is time to immerse ourselves in AR and to define both marker-based and marker-less AR with examples and to show in which applications they can be used.
At the conclusion of this article, one should be well-acquainted with the following AR types and ways to use them efficiently.
What is Marker-Based Augmented Reality?
Image recognition AR often called marker-based AR is a technology that uses certain markers, for instance, QR codes, images, or printed patterns to deliver digital content.
When the camera of the AR device scans these markers, it superimposes the relevant digital info in the real world.
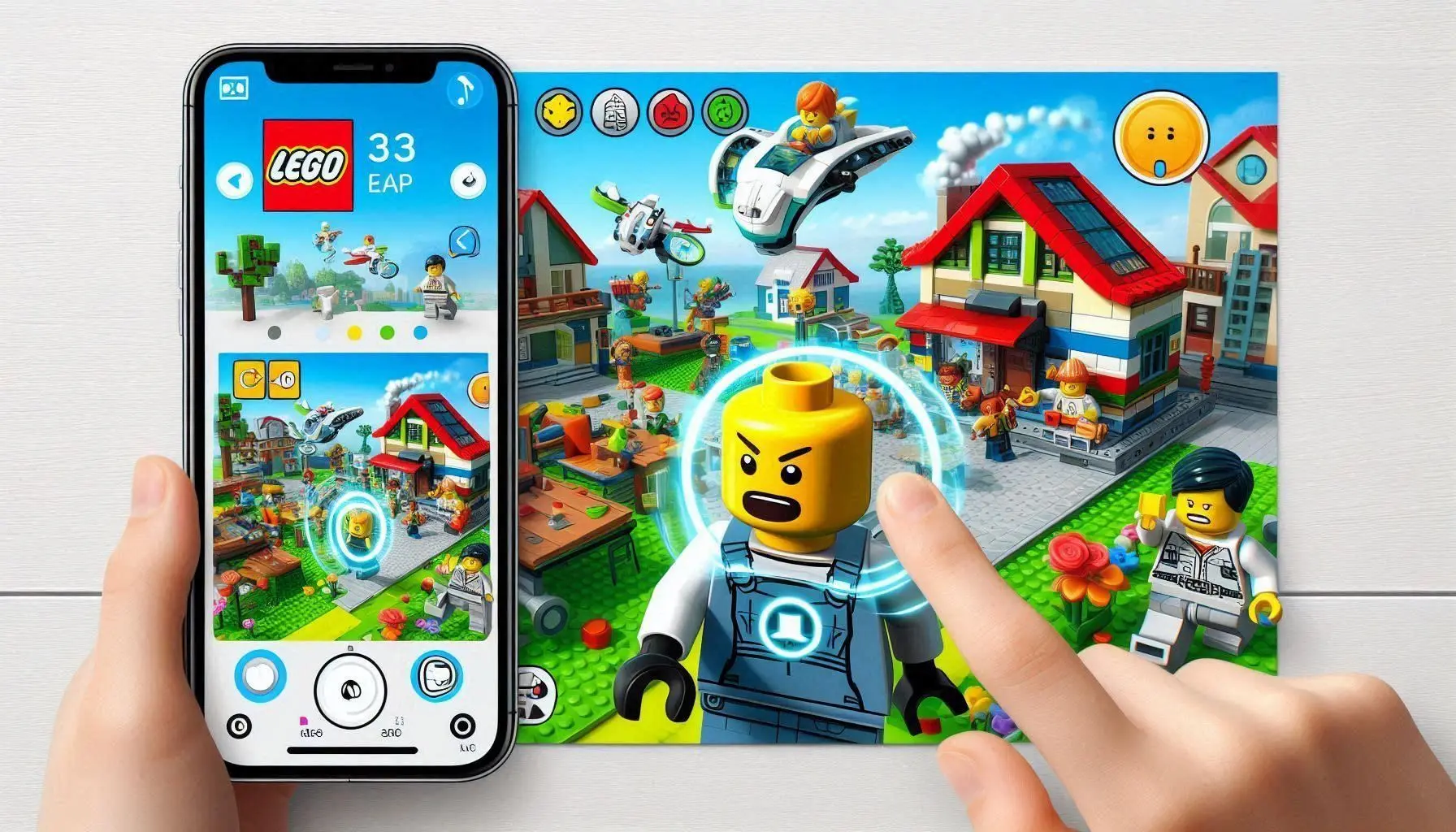
How It Works
- Marker Detection: The camera of the AR device moves and searches for the defined markers within the environment.
- Image Recognition: Each marker found is recognized by the AR software as well as pulling up the relevant content associated with the marker.
- Overlay of Digital Content: The digital content on the other hand is displayed on the real world by the AR device relying on the position and the orientation of the marker.
Pros of Marker-Based AR
- Accuracy: Marker based AR is not easy to move and gets placed and tracked accurately so they give a good and consistent AR experience.
- Simplicity: it is not a complex solution and thus anybody who wants to design or create the solution is able to do so with a lot of ease.
- Reliability: The robustness of marker based AR does not become an issue because as long as the markers are visible and well maintained it runs efficiently in the different environments.
Cons of Marker-Based AR
- Dependency on Markers: The AR experience is in the form of markers which can limit AR applications’ utility and their ability to be easily expanded.
- Aesthetic Limitations: The need for the signs may be introducing or obtrusive which is likely to be disruptive to the appearance and style of the real world setting.
- Maintenance: Markers should be in good shape; thus, they should be replaced when they become weak or unresponsive to the signals.
Examples of Marker-Based AR
Example 1: LEGO AR Play
Marker-based AR is implemented in the Lego AR play app in which the users can scan the Lego sets with the help of a smartphone to view the 3D animations of sets.
This is a plus to the play experience since it incorporates digital which can be incorporated in to the actual LEGO models.
Example 2: Museums and Exhibits
There is a common application of marker-based AR, most of the museums and exhibits introduce their visitors to extra data and execute applications.
Some special markers are placed near the exhibits, by scanning them visitors are able to watch videos, use the audio guide mode, or fill the exhibition with 3D models, which makes the educational process more creative.
What is Markerless Augmented Reality?
Typically, location-based or spatial AR is defined as markerless AR, in which no markers are used to define special areas that call up digital content.
However, it employs the device’s sensors, GPS, along with computer vision for perceiving and enhancing the physical environment. This makes AR to be more flexible and also dynamic.

How It Works
- Environmental Understanding: To comprehend the environment the AR device has sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes and GPS) as well as computer vision algorithms.
- Feature Tracking: This is done through objects recognition where the software is built to track surfaces and other objects in the environment, and spatial coordinates.
- Overlay of Digital Content: It depicts digital information in relation to the aspects found held by the AR device on the physical environment.
Pros of Markerless AR
- Flexibility: Unlike marker-based AR, markerless AR is not confined by markers and can therefore be utilized in more and very different variety of ways and to create all sorts of new experiences.
- Aesthetic Appeal: As the name implies markerless AR does not require the use of markers which helps to retain the aesthetic and natural outlook of the real-world environs.
- Scalability: With markerless AR, the entire space of buildings or even open areas can also be augmented and developed into even more complex picture.
Cons of Markerless AR
- Complexity: Markerless AR uses advanced technology and computer vision and sensors so it is not safe with noobs in the field.
- Resource Intensive: AR without markers can be quite demanding, which means that is takes a lot of processing power and battery energy.
- Variable Accuracy: The major disadvantage of markerless AR is that the accuracy is dependent on the natural environment including light and surface texture.
Examples of Markerless AR
Example 1: Pokémon GO
An example of markerless is Pokémon GO – a mobile game that lets players catch virtual characters in real life.
It employs the location tracking features of the smartphone and the camera in that it places the Pokémon characters on the screen in relation to the player’s physical environment.
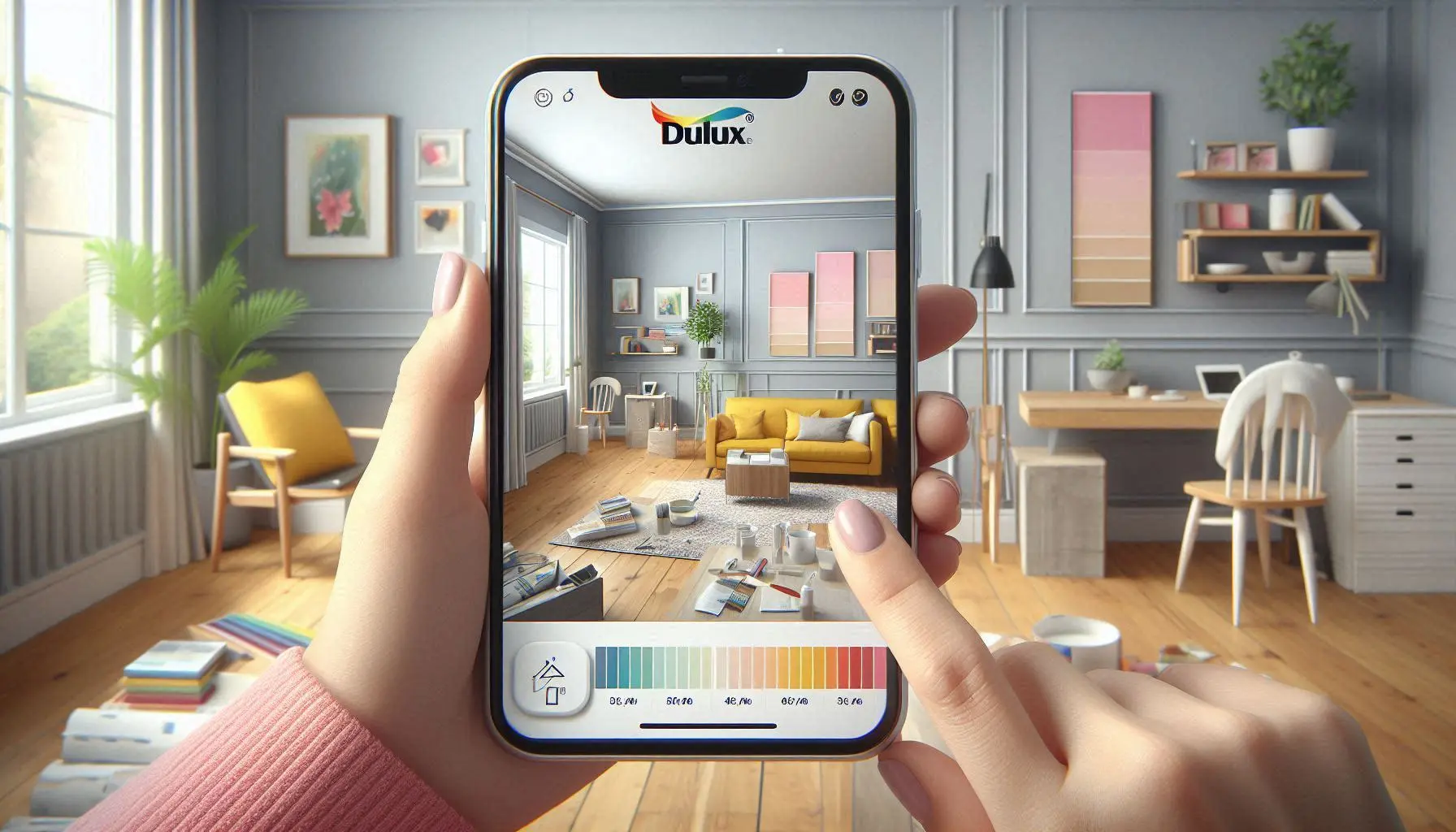
Example 2: IKEA Place
IKEA Place is an application that utilizes augmented reality to give clients an idea of how the IKEA furniture will look in their house.
Through the lens and sensors of the smartphone, the application augments the 3D models of the furniture on the shopping area and in the customers’ homes so that they can make the right choices.
Comparative Analysis
Key Differences
- Dependency on Markers: In Marker-based Augmented Reality there are fixed markers that can be probably set, whereas in Markerless Augmented Reality the environment features and sensors are used.
- Implementation Complexity: Marker-based AR is not very complex to use compared to markerless AR which still needs advanced technology and skilled people.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Compared to marker-based AR, markerless AR is more adaptive and has an unlimited number of possible applications.
- Accuracy and Stability: With marker based Augmented Reality, the tracking is more accurate and stable whereas in marker less AR the tracking depends on the environmental conditions.
Best Use Cases for Each Type
Marker-Based AR:
- Product Demonstrations: Perfect when it comes to advertising products in physical shops because the markers can be placed on the packaging or physical structures where the products are to be sold.
- Education and Training: They are quite helpful when there is a specific area where markers can be placed to help AR go through the experience.
- Events and Exhibitions: Good for adding content which is interactive near the exhibits, using markers close to interactive displays.
Markerless AR:
- Gaming: Ideal for the designing of engaging environments for gaming such as the recently popularized Pokémon GO.
- Home Decor and Furniture: Especially in the applications such as IKEA Place where users are able to place furniture in their home without using markers.
- Navigation and Wayfinding: Most suitable for scenarios in which it is impossible to put markers, for example, in large shops or terminals.
Conclusion
Both marker based and marker less AR have their own merits and demerits and that is why they can be used to serve a purpose for a specific application or use.
Marker-based augmented reality has high accuracy and easy to use that is why it suitable for organized environment and specific use.
However marker less AR is more flexible, scalable and cautiously beautiful and thus suitable for dynamic and large applications require.
This distinction will help businesses and developers decide which of these AR mechanisms to harness to design good and useful AR experiences.
With the future developments of the Augmented Reality technology in mind, there are numerous possible additional and more complex uses that can be expected for the near future, being still also incredibly significant and changing the methods by which humanity engages with its environment.

Thank you for this well-written and informative post. The way you explained the details was very helpful and made the topic much more approachable. I appreciate the effort you put into creating such valuable content.
Great post! The information was clear and very helpful. Thanks for sharing.